The Findings of a Mad Turf Pathologist
go.ncsu.edu/readext?800710
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲Dollar Spot
Weather has been conducive for dollar spot in many areas of the Southeast, especially those that have had some humidity. Humidity in central North Carolina has been minimal as of late, but last week and this week fired up some nice dollar spot pressure. Dollar spot development ebbs and flows based on temperature and relative humidity and if you are interested in understanding when dollar spot pressure is increasing, please check the following website: Dollar Spot Forecast Model. This site is using the Smith-Kerns dollar spot model developed by yours truly and Drs. Damon Smith and Paul Koch. The model accurately predicts dollar spot development and this site also allows for alerts.
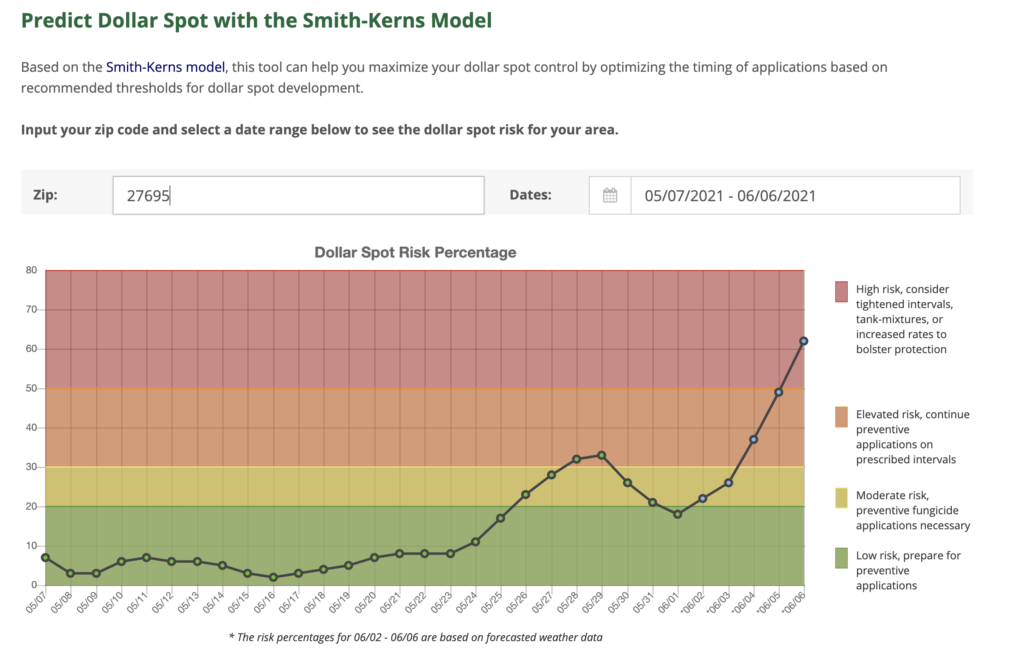
Current dollar spot forecast for Raleigh, NC shows elevated to high risk of development in the coming week.
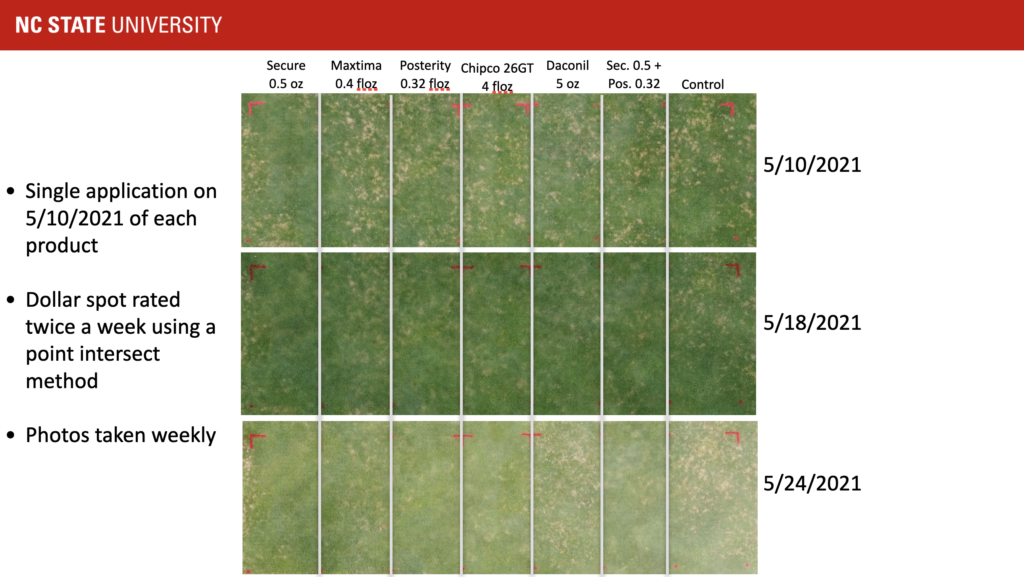
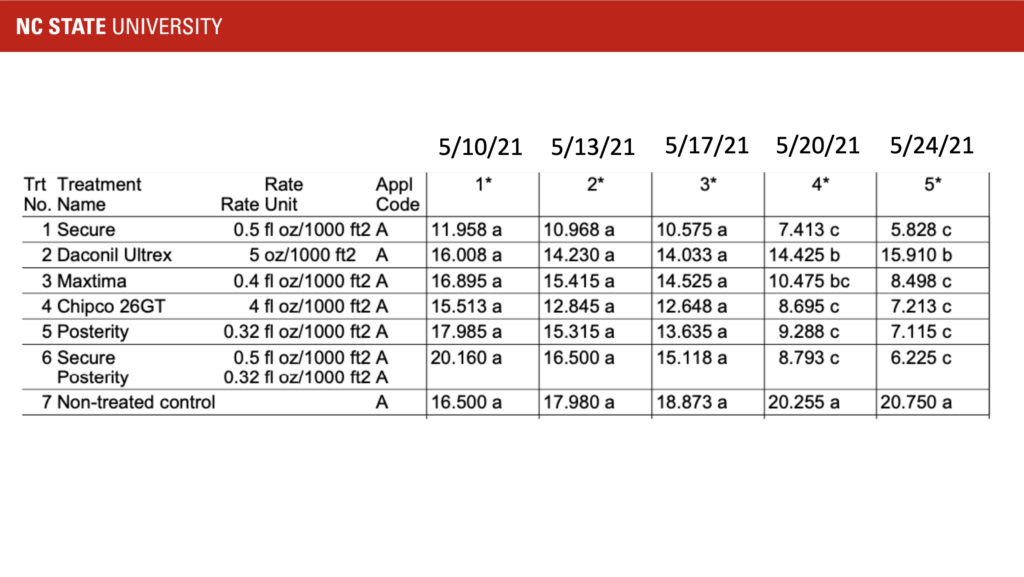
In Raleigh, we had a significant amount of dollar spot develop in late March. The cool, dry April led to very little recovery on our ‘Crenshaw’ creeping bentgrass fairway area. Thus, we decided to test how long curative treatments of fungicides would take to facilitate recovery from dollar spot. We tested Secure, Daconil, Maxtima, Posterity, Iprodione, and Secure tank-mixed with Posterity. Single applications of each fungicide were made on May 10, 2021, and disease was rated twice a week. Even with excellent growing conditions for creeping bentgrass, dollar spot suppression was not detected until 10 days after the application. Although complete suppression had not occurred as of May 24, 2021, Secure, Maxtima, Iprodione, Posterity, and Secure + Posterity continued to improve. Daconil did reduce dollar spot severity when compared to the non-treated control, but had significantly more dollar spot than all the other fungicide treatments.
The moral of the story is to prevent dollar spot development by using the forecasting model or apply before you traditionally see the disease. Curative applications can be effective, but likely take longer than one would think for recovery. If curative applications are necessary, use a systemic product or tank-mix a systemic with a contact fungicide. It is interesting to note that we conducted this study in 2019 and observed similar results. However, during that trial, the weather was not as conducive for creeping bentgrass growth and recovery took 2 weeks. Furthermore, Secure and Daconil (contact fungicides) did not perform well in 2019. It is very interesting that Secure performed well this year given that it is classified as a contact fungicide.
Numerous fungicides perform well for dollar spot suppression and for more information on specific fungicides please check out the dollar spot profile on our website. We are testing a comprehensive fungicide program for dollar spot this year and the treatments are excelling in this trial. It interesting to note that Maxtima alone is doing an outstanding job of suppressing dollar spot, but it is important to rotate chemistries to prevent fungicide resistance development. For those dealing with dollar spot, a strong rotation to consider is a SDHI (many choices), Maxtima, and Secure or chlorothalonil on a 14- or 21-day interval. The beauty of Maxtima and chlorothalonil is they provide protection against anthracnose as well, but a supplemental preventative fungicide or phosphite application maybe necessary if anthracnose pressure is high.
Anthracnose
We have diagnosed foliar anthracnose from numerous golf courses in the Mountains of NC, so pressure must be ideal in more temperate climates. Typically, the crown rot phase of this disease is the most destructive, but samples we have observed were blistered with foliar anthracnose. Luckily this phase of the disease can be overcome with a curative fungicide application and products that have performed best for us are listed on our website. In general, DMIs, Velista, or a phosphite mixed with chlorothalonil will work well for suppressing foliar anthracnose. As heat and humidity continue to increase (nighttime temperatures above 65oF consistently), it is imperative to consistently (every two weeks especially on annual bluegrass or creeping bentgrass putting greens) apply a phosphonate (Signature or Appear) tank-mixed with a contact (chlorothalonil, Secure or mancozeb). Insertions of products that suppress anthracnose should also have summer patch suppression as well. These fungicides can be mixed with products to suppress Pythium root rot as well. Watering in these fungicides (do not water in the phosphonate and contact applications) are necessary to provide protection against summer patch and will not affect anthracnose control.
If you continually struggle with anthracnose at your facility, research from Drs. Bruce Clarke, Jim Murphy and John Inguagiato have clearly identified that nitrogen and potassium are critical for suppression of the disease. Specifically, they demonstrated that nitrogen in the tissue needs to be at or above 3.5% and potassium should be at least 50 ppm in soil or 2% in the tissue. When these levels were attained with these nutrients, anthracnose was significantly reduced. It is amazing during all the visits and travels Lee and I have experienced, it is rare to see severe disease on well-fertilized turf. Just an interesting observation over the course of 15 or 20 years. Of course, sand topdressing is very important for reduction of anthracnose as well. For more information on best management practices for anthracnose, please reference the following article in GCM from Rutgers University –Anthracnose BMPs.